Single Busbar
Advantages
• The control system
is straight forward
• Each bay practically
independent
• No switching in
current transformer (CT) and voltage
transformer (VT) circuits
Drawbacks
• The object, line or
transformer, out of service for
maintenance of the circuit breaker (CB)
• The complete station
is out of service for a busbar fault
Double
busbar
Advantages
• Faults limited to objects on the faulty bus
• Reduced short circuit currents and reduced network disturbance with open bus-coupler
• Busbar
transfer without load interruption
Drawbacks
• The object, line or transformer, out of service for maintenance of the circuit breaker (CB)
• Bus voltage and breaker failure trip requires selection circuits
• Switching of busbar
CTs, tripping and interlocking circuits
Transfer busbar
Advantages
• Maintenance of 1 CB without load interruption
• No switching in CT and VT circuits
Drawbacks
• Switching in trip and autoreclosing circuits
• Only one bay can be connected to the transfer bus
• The complete station
is out of service for a busbar fault
Ring
busbar
Advantages
• Operation can be maintained with 1 circuit breaker
(CB) out of service
• Simple interlocking
Drawbacks
• Two CBs have to be
tripped at a primary fault
• Autoreclosing of two CBs in sequence
• Summation of CTs required
• Switching in VT circuits
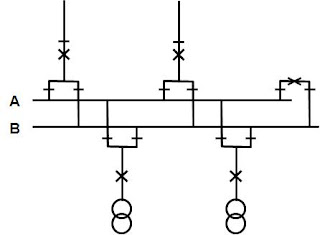
1 1/2 breaker busbar
Advantages
• Operation can be
maintained with 1 circuit breaker (CB) out of service
• Simple interlocking
• No switching in
current transformer (CT) circuits
Drawbacks
• Two CBs have to be
tripped at a primary fault
• Autoreclosing of two CBs in sequence
• Summation of CTs
necessary





1 comment:
Thank you Murugan, for this info
Post a Comment